TaTME into detail..
Sami Chadi
Joep Knol
The transanal total mesorectal excision (TaTME) is a procedure that optimizes the selection of ones distal margin and potentially improves the rate of mesorectal completeness when performing a proctectomy.
The novel nature of the procedure demands large volume database assessments (LOREC database - UK, OSTRiCh database - USA) as well as randomized trials (COLOR III) to allow for the appropriate assessment of the feasibility and suitability of this procedure.
Didactic and hands-on courses are necessary to provide interested surgeons with the knowledge and initial expertise when considering the introduction of this procedure into ones practice.
Courses can exist in different formats including didactic components in combination with observing live-surgery, dry-lab practice and hands-on proctored cadaveric components.
Importantly, it should be stressed that interested surgeons should have a significant expertise and experience in laparoscopically managing patients with rectal cancer with some experience in transanal endoscopic techniques.
Attending courses with surgeon-partners also planning on performing this procedure will allow for a collaborative phasing in of the technique in both practices. At course completion, surgeons are tasked with selecting the appropriate patients for the initial part of their series.
We would stress ensuring that these initial cases are done by surgeons in a group so as to assist one another, as well as ensuring that part of ones early experience is proctored to assist with the early learning curve as well as to avoid any of the potential risks of the procedure.
This algorithmic approach to the introduction of this important skill-set into ones practice will likely result in a safe and ethically appropriate initiation of ones experience.
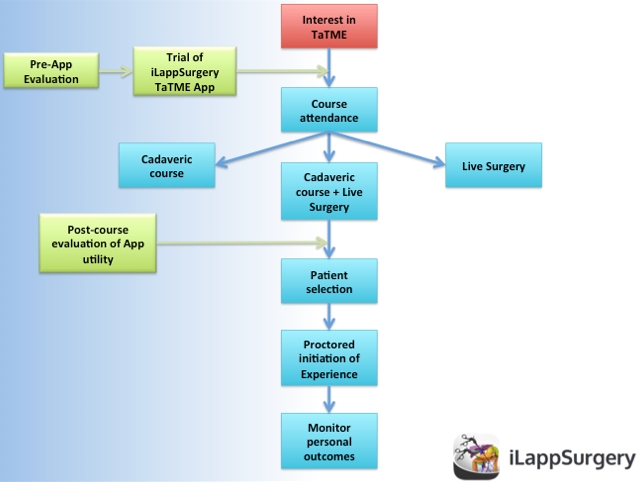
We feel that the iLappSurgery TaTME module will serve as a helpful adjunct for surgeons considering integrating the TaTME procedure into practice by assisting with pre-course preparation and maintenance of knowledge in the post-course period; we would strongly advise against substituting this module for any part of the aforementioned algorithmic approach.
In chapter 7A we discuss the OR set-up and patient installation.
In the following chapters we aim to describe the stepwise approach to TaTME.
Also the dissection proceeds in a standardized manner.
Starting posteriorly, dissection is carried out perpendicularly through the rectal wall to the mesorectal fascia. This requires quite a steep turn posteriorly in order to enter the mesorectal plane distally and excise the entire mesorectum.
Dissection then continues up through the TME dissection plane in the retro-rectal space between the mesorectal fascia and the parietal pelvic fascia, which contains the pelvic autonomic nerves.
Anterior dissection is then performed in the rectovaginal septum or in the rectoprostatic plane.
Lateral dissection is purposely left to last because prior dissection of the posterior and anterior planes help to differentiate the mesorectum from the lateral side wall at that level. When the lateral dissection is nearing completion, the peritoneal cavity is entered from below, often anteriorly, and the pneumoperitoneum is established in continuity with the pneumopelvis. Any remaining tissue bridges are divided, to complete the dissection; in a synchronized dissection this can be done from both sides, and the last part of the lateral dissection can be facilitated by traction from both the abdominal and transanal surgeons.
The specimen is then extracted transanally or through the abdomen, depending on the surgeon’s choice. It is imperative that the specimen is handled with great care in order not to damage the mesorectal envelope. Bulky tumours are probably best extracted via an abdominal incision with an appropriate wound protector. If an abdominal extraction site is to be used, the left flank trocar incision can be enlarged and protected for specimen extraction or a small pfannensteil / suprapubic or right iliac fossa incision can be used.
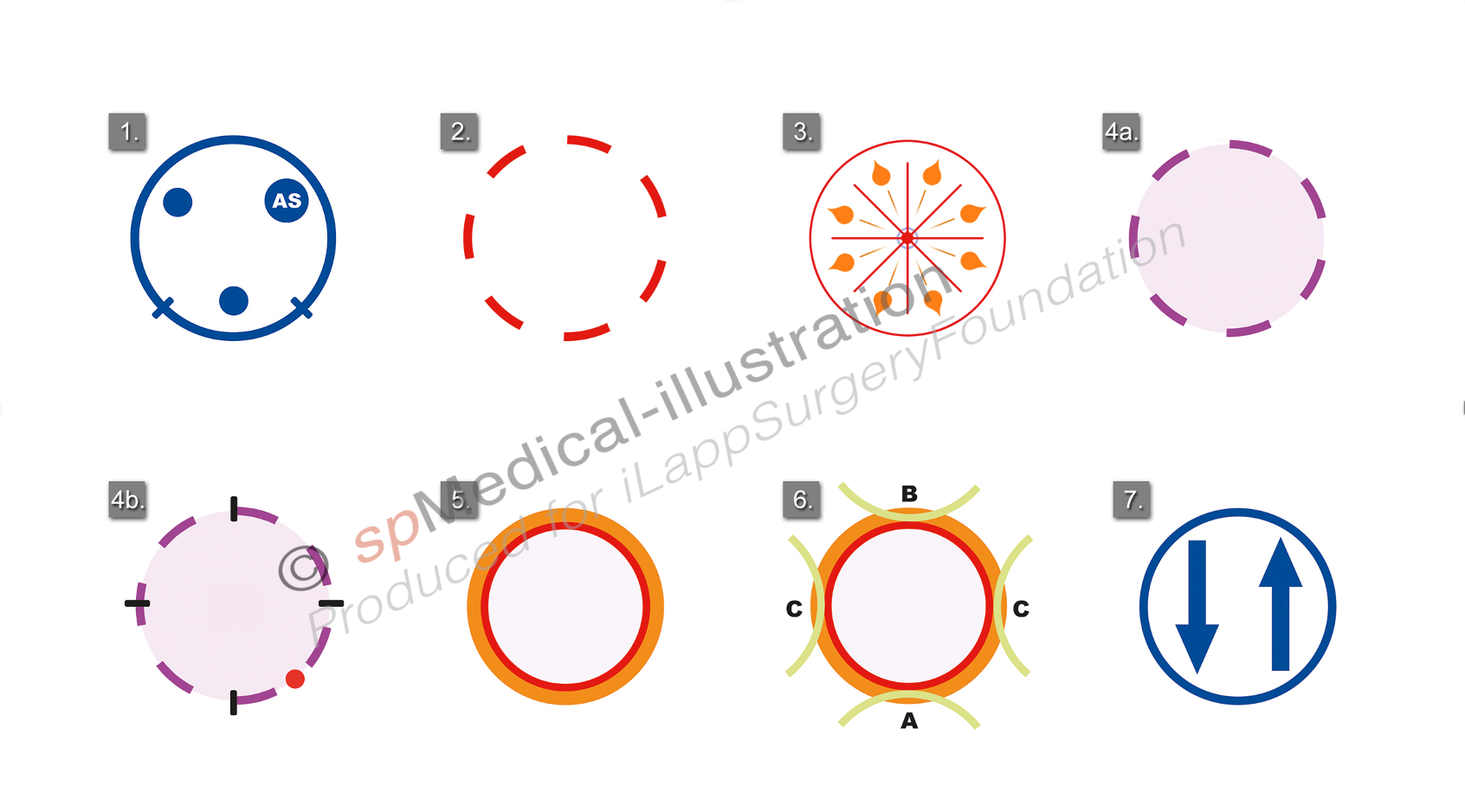
1. Installation of platform and trocars
2. Placement of pursestring
3. Washout
4a. Marking the line of rectotomy
4b. Starting the rectotomy
5. Full thickness dissection
6. Order of dissection
7. Specimen extraction and reanastomosis